A network with the topology
![]() , the input nodes
, the input nodes ![]() and
the output nodes
and
the output nodes ![]() is called a feed forward network if it
satisfies the following three conditions:
is called a feed forward network if it
satisfies the following three conditions:
Since the network is supposed to be acyclic, the output state is a direct
function of the input state. This network function ![]() defines the functionality
of the network.
defines the functionality
of the network.
A feed forward network with the topology
![]() ,
the input nodes
,
the input nodes ![]() and the output nodes
and the output nodes ![]() is called
a n-layer network if it satisfies the following conditions:
is called
a n-layer network if it satisfies the following conditions:
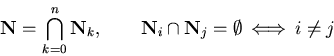
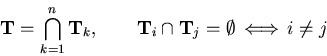
Note that the input layer ![]() is not counted as a real layer,
since their propagation functions are merely constants set to the
components of the input vector.
is not counted as a real layer,
since their propagation functions are merely constants set to the
components of the input vector.
The partitions ![]() can also be expressed my an adjacence matrix
can also be expressed my an adjacence matrix ![]() which
is defined follows:
which
is defined follows:

If
![]() , the layers
, the layers ![]() and
and
![]() are fully connected.
are fully connected.